Back to AI Flashcard MakerBiology /AP® Biology - Cell Structure Part 4
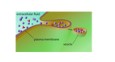
Define: pinocytosis
It is a type of endocytosis. In this process, the cell membrane engulfs the extracellular fluid, as well as the small particles it contains, in a vesicle. Other types of endocytosis include phagocytosis and receptor-mediated endocytosis.
Tap or swipe ↕ to flip
Swipe ←→Navigate
1/10
Key Terms
Term
Definition
Define: pinocytosis
It is a type of endocytosis. In this process, the cell membrane engulfs the extracellular fluid, as well as the small particles it contains, in a vesi...
Define: bulk flow
It is the movement of molecules (typically fluid molecules) in one direction in response to pressure. A classic example is the movement of blood throu...
What term describes diffusion between two regions in which fluids are flowing in opposite directions?
Countercurrent exchange This form of transport allows for a fairly consistent difference in concentration gradient between the two regions, maximizing...
What term is given to the separation of molecules based on their differing abilities to diffuse through a semipermeable membrane?
Dialysis In a dialysis procedure, large particles are unable to diffuse through the dialysis membrane, so small particles are left to diffuse in an at...
Name the three distinct junctions that separate the cells of vertebrates.
tight junctions desmosomes gap junctions These are the three main types of cell junction to know for the AP Biology exam.
What features characterize tight junctions?
They are composed of multiple proteins, including claudins, and form an impermeable seal between adjacent cells. This prevents fluid and solutes from ...
Related Flashcard Decks
Study Tips
- Press F to enter focus mode for distraction-free studying
- Review cards regularly to improve retention
- Try to recall the answer before flipping the card
- Share this deck with friends to study together
| Term | Definition |
|---|---|
Define: pinocytosis | It is a type of endocytosis. In this process, the cell membrane engulfs the extracellular fluid, as well as the small particles it contains, in a vesicle. Other types of endocytosis include phagocytosis and receptor-mediated endocytosis. |
Define: bulk flow | It is the movement of molecules (typically fluid molecules) in one direction in response to pressure. A classic example is the movement of blood through blood vessels. Blood, like typical fluids, tends to travel from areas of high pressure to areas of low pressure. |
What term describes diffusion between two regions in which fluids are flowing in opposite directions? | Countercurrent exchange This form of transport allows for a fairly consistent difference in concentration gradient between the two regions, maximizing diffusion. A classic example of this mechanism occurs in the loop of Henle, a region of the nephron (the structural unit of the kidney). |
What term is given to the separation of molecules based on their differing abilities to diffuse through a semipermeable membrane? | Dialysis In a dialysis procedure, large particles are unable to diffuse through the dialysis membrane, so small particles are left to diffuse in an attempt to reduce the overall concentration gradient between the compartments. This technique is often used to remove toxins from the blood in cases of kidney failure. |
Name the three distinct junctions that separate the cells of vertebrates. | tight junctions desmosomes gap junctions These are the three main types of cell junction to know for the AP Biology exam. |
What features characterize tight junctions? | They are composed of multiple proteins, including claudins, and form an impermeable seal between adjacent cells. This prevents fluid and solutes from going "around" the cell to enter a cavity. Tight junctions are found between cells in the same epithelial layer. |
What features characterize gap junctions? | They are small channels formed from connexin proteins. They allow small solutes and fluid to pass from one cell to another. While gap junctions are found between most cells, they are generally associated with cells that must communicate or function together, like neurons. |
What features characterize desmosomes? | They are composed of intermediate filaments and are found at localized regions throughout a cell's membrane. They generally attach one epithelial or cell layer to another. Desmosomes are found in epithelial and muscle tissue. |
Which type of junction is especially important in the heart? | Gap junctions The electrical impulse that triggers contraction must travel throughout the entire heart muscle, beginning at the SA node. Gap junctions facilitate the movement of ions, allowing the cells to act together as one unit. |
What factor plays the biggest role in limiting the size of a cell? | The cell must have a sufficiently large surface area-to-volume ratio. As the cell becomes larger, volume increases faster than surface area, causing this ratio to decrease. A large surface area gives the cell a greater ability to obtain nutrients and eliminate waste through its cell membrane. |