How do Ca2+ ions facilitate actin-myosin binding?
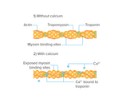
Each calcium ion binds to troponin, causing tropomyosin to change its shape. This frees the myosin binding site on the relevant actin molecule.
When calcium is not present, tropomyosin is bound to actin in a position that blocks the myosin binding site. For contraction to occur, this site must be open for the head of a myosin molecule to attach.
Key Terms
How do Ca2+ ions facilitate actin-myosin binding?
Each calcium ion binds to troponin, causing tropomyosin to change its shape. This frees the myosin binding site on the relevant actin molecule.
...What is the function of the T-tubule system in skeletal muscle?
These are deep folds in the sarcolemma of muscle cells. Since they bring the cell membrane closer to the central regions of the cell, they allow ac...
What name is given to the current model of skeletal muscle contraction?
sliding filament model
According to this theory, myosin heads bind to actin molecules, then undergo a quick stroke to shorten the sarcomere. ...
Which of the following does not change in length during contraction: the A band, the I band, or the H zone?
The length of the A band remains unchanged. In a sarcomere, the A band refers to the length of an entire myosin fiber. Since actin and myosin do no...
Which of the following does change in length during contraction: the A band, the I band, or the H zone?
Both the I band and the H zone change in length during contraction. In a sarcomere, the I band refers to the unoverlapped actin region, while the H...
In skeletal muscle, how does the role of tropomyosin differ from that of troponin?
Tropomyosin directly attaches to actin. In the absence of calcium, it physically blocks the myosin binding site.
Troponin bi...
Related Flashcard Decks
Study Tips
- Press F to enter focus mode for distraction-free studying
- Review cards regularly to improve retention
- Try to recall the answer before flipping the card
- Share this deck with friends to study together
| Term | Definition |
|---|---|
How do Ca2+ ions facilitate actin-myosin binding? | Each calcium ion binds to troponin, causing tropomyosin to change its shape. This frees the myosin binding site on the relevant actin molecule. When calcium is not present, tropomyosin is bound to actin in a position that blocks the myosin binding site. For contraction to occur, this site must be open for the head of a myosin molecule to attach. |
What is the function of the T-tubule system in skeletal muscle? | These are deep folds in the sarcolemma of muscle cells. Since they bring the cell membrane closer to the central regions of the cell, they allow action potentials to quickly propagate to the sarcomeres. |
What name is given to the current model of skeletal muscle contraction? | sliding filament model According to this theory, myosin heads bind to actin molecules, then undergo a quick stroke to shorten the sarcomere. The filaments themselves do not change in length during this process; they simply overlap. |
Which of the following does not change in length during contraction: the A band, the I band, or the H zone? | The length of the A band remains unchanged. In a sarcomere, the A band refers to the length of an entire myosin fiber. Since actin and myosin do not actually shorten during contraction, the A band's length is always constant. |
Which of the following does change in length during contraction: the A band, the I band, or the H zone? | Both the I band and the H zone change in length during contraction. In a sarcomere, the I band refers to the unoverlapped actin region, while the H zone refers to the region that contains myosin alone. Contraction involves the overlapping of filaments, so both of these regions shorten as the actin and myosin pull together. |
In skeletal muscle, how does the role of tropomyosin differ from that of troponin? |
|
Briefly list the steps involved in skeletal muscle contraction, beginning with the influx of Ca2+ into the sarcoplasm. |
|
After death, the cells of the body no longer synthesize ATP. What effect does this have on the condition of skeletal muscle? | Skeletal muscle becomes permanently contracted in a condition known as rigor mortis. A common misconception is that ATP is necessary for the initiation of muscle contraction. Technically, ATP is required for the termination of contraction, where myosin dissociates from actin. Deceased individuals would be unable to perform this process, so their muscles would remain contracted. |
What main functions are served by the skeletal system? |
|
Name the two major types of bone. |
Compact bone is also called cortical bone; spongy bone is also called cancellous bone. |
What features characterize compact bone? | It is hard and dense, mainly composed of the minerals, salts, and collagen that form the bony matrix. Compact bone is comprised of cylindrical subunits called osteons. |
What features characterize spongy bone? | It is softer and less dense than compact bone. It contains many blood vessels, as well as gaps in its structure that are filled with bone marrow. Spongy bone is comprised of thin, sharp subunits called trabeculae. |
Label the following parts of a long bone on the diagram below: epiphysis, diaphysis, compact bone, spongy bone, periosteum. | |
The diagram below shows the microscopic anatomy of the bony matrix. Label the following structures: osteon, trabeculae, Haversian canal, lamellae. | |
Define: tendon | A strip of tough connective tissue that connects a muscle to a bone. Tendons are composed of collagen. Tendons generally function to facilitate movement. |
Define: ligament | A strip of tough connective tissue that connects a bone to another bone. Ligaments are composed of collagen. Ligaments generally function to stabilize joints. For example, the anterior cruciate ligament, or ACL, stabilizes the knee. |
What is cartilage, and what substances does it include? | A form of connective tissue that is less rigid than bone. It includes elastin protein fibers, proteoglycan, and collagen. The collagen in cartilage is produced by specialized cells called chondrocytes. |
What functions does cartilage serve in the human body? | During development, cartilage solidifies into bone in a process known as ossification. It also provides soft, flexible protection for certain parts of the anatomy. For example, the trachea, nose, and ears contain cartilage. |
What broad term can be used to describe the skeleton of a horse? | endoskeletons An endoskeleton is an internal rigid structure. It can provide support to the organism, but does not encase the entire body. |
What broad term can be used to describe the skeleton of a lobster? | exoskeletons An exoskeleton is an external rigid encasement. It protects the entirety of the body, but must be replaced as the organism grows. |
The human skeleton can be split into which two major divisions? |
The axial skeleton is relatively central; it contains the vertebrae, ribcage, and skull. The appendicular skeleton is more peripheral and includes the bones of the appendages and the pelvis. |
Regulation of which ion involves both the skeletal and endocrine systems? | calcium Plasma Ca2+ concentration is controlled by two hormones: calcitonin and parathyroid hormone (PTH). Calcitonin lowers plasma calcium by promoting its storage in bone, while PTH has the opposite effect. |
How does the role of an osteoclast differ from that of an osteoblast? |
|
What effect would excess production of calcitonin have on plasma calcium levels? | decrease Calcitonin is released from the thyroid when plasma calcium levels are high. It stimulates osteoblasts to increase bone formation, taking calcium out of the blood in the process. In contrast, parathyroid hormone stimulates osteoclasts. |
When a bone sample from a certain patient was analyzed, unusually high osteoblast activity was observed. In which hormone might this patient be deficient? | parathyroid hormone | PTH Abnormally high osteoblast activity means that excess calcium is being taken out of the plasma and stored as bone. This can result from high levels of calcitonin or low levels of PTH. |
What is the main mineral component of bone, and what is its chemical formula? | hydroxyapatite (Ca5(PO4)3OH). It is important to know that bone contains calcium, phosphate, and hydroxide. |
What name classifies movable joints that contain closed regions filled with lubricating fluid? | synovial joints Synovial joints allow for flexibility at the junctions between bones. The rigid bones are separated by synovial fluid. Ball-and-socket joints are an example of this type of structure. |