Biology 101 - Reproductive System and Development Part 3
This deck covers key concepts related to the reproductive system and embryonic development, including hormonal changes during pregnancy, cell differentiation, and the formation of germ layers.
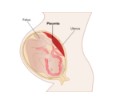
Define: placenta
The organ through which a fetus obtains nutrients and performs gas exchange.
The placenta also performs endocrine functions, secreting estrogen, progesterone, and hCG.
Key Terms
Define: placenta
The organ through which a fetus obtains nutrients and performs gas exchange.
The placenta also performs endocrine functions, secreting estrog...
A woman is midway through her second trimester of pregnancy. Which of her hormones will be present at high levels?
Estrogen
progesterone
hCG
In early pregnancy, progesterone and some estrogen are secreted by the corpus luteum. Within the third ...
The end of pregnancy is marked by a series of uterine contractions, leading to the expulsion of the fetus through the birth canal. Which two interchangeable terms describe this process?
Parturition or birth
The repeated contractions that lead to the birth of the fetus are known as labor.
Which hormone, released from the anterior pituitary, promotes lactation after birth?
prolactin
On the diagram below, label the testes, epididymis, vas deferens, prostate gland, and urethra.
What is the function of the scrotum?
It holds the testes, sits outside the body. This keeps the testes at a temperature slightly lower than 37º C, facilitating spermatogenesis.
Related Flashcard Decks
Study Tips
- Press F to enter focus mode for distraction-free studying
- Review cards regularly to improve retention
- Try to recall the answer before flipping the card
- Share this deck with friends to study together
| Term | Definition |
|---|---|
Define: placenta | The organ through which a fetus obtains nutrients and performs gas exchange. The placenta also performs endocrine functions, secreting estrogen, progesterone, and hCG. |
A woman is midway through her second trimester of pregnancy. Which of her hormones will be present at high levels? | Estrogen progesterone hCG In early pregnancy, progesterone and some estrogen are secreted by the corpus luteum. Within the third month, the placenta becomes the main source of these hormones, as well as hCG. |
The end of pregnancy is marked by a series of uterine contractions, leading to the expulsion of the fetus through the birth canal. Which two interchangeable terms describe this process? | Parturition or birth The repeated contractions that lead to the birth of the fetus are known as labor. |
Which hormone, released from the anterior pituitary, promotes lactation after birth? | prolactin |
On the diagram below, label the testes, epididymis, vas deferens, prostate gland, and urethra. | |
What is the function of the scrotum? | It holds the testes, sits outside the body. This keeps the testes at a temperature slightly lower than 37º C, facilitating spermatogenesis. |
What process occurs in the epididymis? | The sperm become fully mature and motile. This structure also stores sperm after they are made. |
Name two male reproductive glands and describe their functions. | Prostate gland secretes a basic solution that protects the sperm from acidic conditions. Bulbourethral or Cowper's glands produce a lubricating fluid prior to ejaculation. |
Define: zygote | It is the diploid cell created when a sperm cell fertilizes an ovum. Note that a zygote is single-celled; once it undergoes a single division, it will be called an embryo. |
Trace the path of a zygote from the point of fertilization to the point of implantation. What structures does it encounter? | Fertilization occurs in the Fallopian tubes. From there, the zygote travels directly to the uterus and implants in the endometrium, or uterine lining. |
By which process does an embryo increase its number of cells, but not its overall size? | The early divisions of the embryo are referred to as cleavage. In this process, the cells divide very quickly without growing between divisions. The regular cell cycle includes two rest or "gap" phases, G1 and G2. During cleavage, dividing cells skip these phases. |
Define: morula | The name given to the embryo after multiple cleavage divisions. This structure is extremely dense. The morula later develops into the blastula. |
What is a blastocyst, and from what other structure does it arise? | A hollow cell arrangement that develops from the morula. A blastocyst contains a central blastocoel, a dense inner cell mass, and a surrounding trophoblast. |
What is gastrulation, and which germ cell layers does it produce? | It is the differentiation of the blastula into three distinct layers: the ectoderm, the mesoderm, and the endoderm. |
Define: ectoderm | It is the outermost germ layer formed during development. Structures arising from the ectoderm include the eyes, skin, hair, nails, and nervous system. |
Define: mesoderm | It is the middle germ layer formed during development. Structures arising from the mesoderm include blood vessels, gonads, and the muscular and skeletal systems. Note that the kidneys also derive from mesoderm, not endoderm. |
Define: endoderm | It is the innermost germ layer formed during development. Structures arising from the endoderm include internal organs such as the pancreas and urinary bladder. The endoderm also gives rise to the linings of the digestive tract and lungs. |
A student asserts that the endoderm gives rise to internal organs like the pancreas, lungs, kidneys, and urinary bladder. About which structure was the student incorrect? | The student was wrong about the kidneys, which develop from the mesoderm. The remaining organs (pancreas, lungs, and urinary bladder) do arise from the endoderm. |
What process involves the differentiation of ectodermal tissue into the structures that will become the nervous system? | neurulation The final product of neurulation is the neural tube, which develops into the central nervous system. Peripheral nervous structures arise from cells of the neural crest. |
Briefly describe the steps involved in neurulation. | The notochord, a long, cylindrical structure related to the backbone, forms. The neural plate (ectoderm lying above the notochord) begins pinching inward to create neural folds. The neural folds meet, forming the neural tube. Neural crest cells move away to form peripheral structures. |
After what amount of time has the zygote progressed into an embryo? Into a fetus? | The zygote is considered an embryo after its first cell division. The embryo is classified as a fetus the beginning of the third month of pregnancy, specifically after the eighth week following fertilization. Estrogen's activity prior to ovulation is one of the few examples of positive feedback. Less common examples include thrombin's role in blood clotting and the effect of oxytocin during labor. |
With regard to development, what is determination? | It refers to the limitation of a cell's potential fate in the body. Determination does not actually change cells into a specific tissue type; it simply restricts what these cells can be. |
With regard to development, what is differentiation? | It refers to actual changes in a cell's gene expression that cause it to assume a specific cell type. For example, the differentiation of a muscle cell might involve changes in cell size, protein production, and responsiveness to signals. |
Define: stem cell | An undifferentiated cell that can either develop into a variety of cell types itself, or produce other cells that can then differentiate further. |
Which cell is more restricted in its development: a pluripotent or a multipotent cell? | multipotent cell Pluripotent cells can develop into any cell type, such as muscle, epithelial, or nervous tissue. These differentiate into multipotent stem cells, which can only give rise to cells of a particular type. |
In which situations might a cell undergo apoptosis? | Apoptosis, or programmed cell death, generally occurs in damaged cells. However, it can also serve as a normal part of development. Viral infection, UV-induced damage, and hypoxia can all induce apoptosis. |