QQuestionAnatomy and Physiology
QuestionAnatomy and Physiology
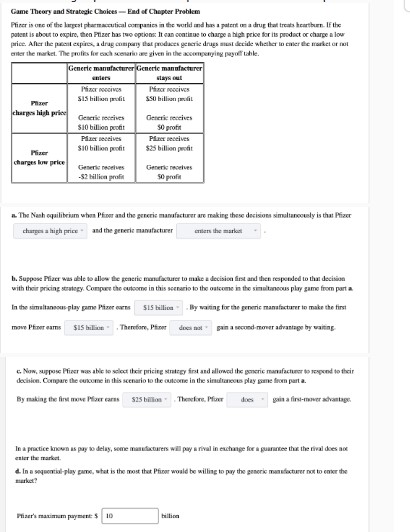
# Game Theory and Strategic Choices - End of Chapter Problem
Pfizer is one of the largest pharmaceutical companies in the world and has a patent on a drug that treats heartburn. If the patent is about to expire, then Pfizer has two options: It can continue to charge a high price for its product or charge a low price. After the patent expires, a drug company that produces generic drugs must decide whether to enter the market or not enter the market. The profits for each scenario are given in the accompanying payoff table.
| | Generic manufacturer | Generic manufacturer |
| --- | --- | --- |
| | | 2020 - 04 |
| Pfizer charges high price | Pfizer receives | Pfizer receives |
| | $\$ 1$ billion profit | $\$ 1$ billion profit |
| | Generic receives | Generic receives |
| | $\$ 1$ billion profit | 50 profit |
| Pfizer charges low price | Pfizer receives | Pfizer receives |
| | $\$ 1$ billion profit | $\$ 1$ billion profit |
| | Generic receives | Generic receives |
| | - $\$ 1$ billion profit | 50 profit |
a. The Nash equilibrium when Pfizer and the generic manufacturer are making these decisions simultaneously is that Pfizer charges a high price - and the generic manufacturer enters the market. b. Suppose Pfizer was able to allow the generic manufacturer to make a decision first and then responded to that decision with their pricing strategy. Compare the outcome in this scenario to the outcome in the simultaneous play game from part a.
In the simultaneous play game Pfizer earns $\$ 1$ billion - By waiting for the generic manufacturer to make the first move Pfizer earns $\$ 1$ billion - Therefore, Pfizer does not - gain a second-mover advantage by waiting. c. Now, suppose Pfizer was able to select their pricing strategy first and allowed the generic manufacturer to respond to their decision. Compare the outcome in this scenario to the outcome in the simultaneous play game from part a.
By making the first move Pfizer earns $\$ 1$ billion - Therefore, Pfizer does - gain a first-mover advantage.
In a practice known as pay to delay, some manufacturers will pay a rival in exchange for a guarantee that the rival does not enter the market. d. In a sequential play game, what is the most that Pfizer would be willing to pay the generic manufacturer not to enter the market?
Pfizer's maximum payment: $\$ 1$ billion
Attachments
6 months agoReport content
Answer
Full Solution Locked
Sign in to view the complete step-by-step solution and unlock all study resources.
Step 1I'll solve this game theory problem step by step, using precise LaTeX formatting:
Step 2: Analyze the Simultaneous Play Game
Where (Pfizer's payoff, Generic's payoff) are shown in $$\$ \text{billions}$$.
In the simultaneous play scenario, we'll construct the payoff matrix: \begin{array}{c|c|c|} & \text{Generic Enters} & \text{Generic Stays Out} \ \hline \text{High Price} & (15, 10) & (30, 0) \ \hline \text{Low Price} & (10, - 2) & (25, 50) \ \hline \end{array}
Final Answer
- Simultaneous Play Nash Equilibrium: (High Price, Enter) - First-Mover Advantage: Pfizer gains by choosing low price first - Maximum Payment to Prevent Market Entry: \$ 15 \text{ billion}
Need Help with Homework?
Stuck on a difficult problem? We've got you covered:
- Post your question or upload an image
- Get instant step-by-step solutions
- Learn from our AI and community of students