QQuestionAnatomy and Physiology
QuestionAnatomy and Physiology
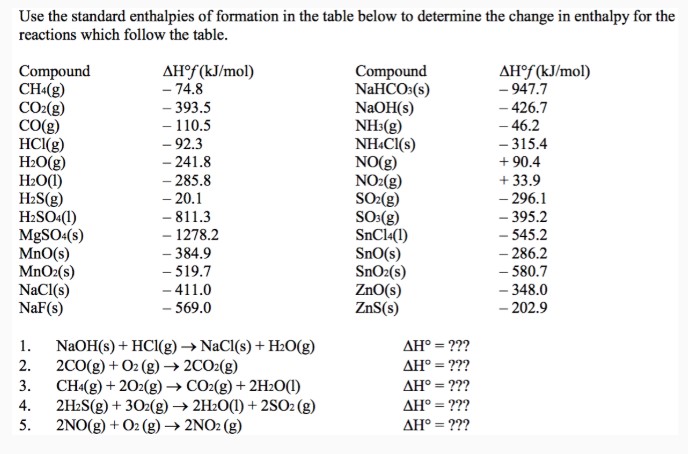
Use the standard enthalpies of formation in the table below to determine the change in enthalpy for the reactions which follow the table.
| Compound | $\Delta \mathrm{H}^{\circ} f(\mathrm{~kJ} / \mathrm{mol})$ | Compound | $\Delta \mathrm{H}^{\circ} f(\mathrm{~kJ} / \mathrm{mol})$ |
| --- | --- | --- | --- |
| $\mathrm{CH}_{4}(\mathrm{~g})$ | - 74.8 | $\mathrm{NaHCO}_{3}(\mathrm{~s})$ | - 947.7 |
| $\mathrm{CO}_{2}(\mathrm{~g})$ | - 393.5 | $\mathrm{NaOH}(\mathrm{s})$ | - 426.7 |
| $\mathrm{CO}(\mathrm{g})$ | - 110.5 | $\mathrm{NH}_{3}(\mathrm{~g})$ | - 46.2 |
| $\mathrm{HCl}(\mathrm{g})$ | - 92.3 | $\mathrm{NH}_{4} \mathrm{Cl}(\mathrm{s})$ | - 315.4 |
| $\mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{O}(\mathrm{g})$ | - 241.8 | $\mathrm{NO}(\mathrm{g})$ | + 90.4 |
| $\mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{O}(\mathrm{l})$ | - 285.8 | $\mathrm{NO}_{2}(\mathrm{~g})$ | + 33.9 |
| $\mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{~S}(\mathrm{~g})$ | - 20.1 | $\mathrm{SO}_{2}(\mathrm{~g})$ | - 296.1 |
| $\mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{SO}_{4}(\mathrm{l})$ | - 811.3 | $\mathrm{SO}_{2}(\mathrm{~g})$ | - 395.2 |
| $\mathrm{MgSO}_{4}(\mathrm{~s})$ | - 1278.2 | $\mathrm{SnCl}_{4}(\mathrm{l})$ | - 545.2 |
| $\mathrm{MnO}(\mathrm{s})$ | - 384.9 | $\mathrm{SnO}(\mathrm{s})$ | - 286.2 |
| $\mathrm{MnO}_{2}(\mathrm{~s})$ | - 519.7 | $\mathrm{SnO}_{2}(\mathrm{~s})$ | - 580.7 |
| $\mathrm{NaCl}(\mathrm{s})$ | - 411.0 | $\mathrm{ZnO}(\mathrm{s})$ | - 348.0 |
| $\mathrm{NaF}(\mathrm{s})$ | - 569.0 | $\mathrm{ZnS}(\mathrm{s})$ | - 202.9 |
| 1. $\mathrm{NaOH}(\mathrm{s})+\mathrm{HCl}(\mathrm{g}) \rightarrow \mathrm{NaCl}(\mathrm{s})+\mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{O}(\mathrm{g})$ | | $\Delta \mathrm{H}^{\circ}=$ ??? | |
| 2. $2 \mathrm{CO}(\mathrm{g})+\mathrm{O}_{2}(\mathrm{~g}) \rightarrow 2 \mathrm{CO}_{2}(\mathrm{~g})$ | | $\Delta \mathrm{H}^{\circ}=$ ??? | |
| 3. $\mathrm{CH}_{4}(\mathrm{~g})+ 2 \mathrm{O}_{2}(\mathrm{~g}) \rightarrow \mathrm{CO}_{2}(\mathrm{~g})+ 2 \mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{O}(\mathrm{l})$ | | $\Delta \mathrm{H}^{\circ}=$ ??? | |
| 4. $2 \mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{~S}(\mathrm{~g})+ 3 \mathrm{O}_{2}(\mathrm{~g}) \rightarrow 2 \mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{O}(\mathrm{l})+ 2 \mathrm{SO}_{2}(\mathrm{~g})$ | | $\Delta \mathrm{H}^{\circ}=$ ??? | |
| 5. $2 \mathrm{NO}(\mathrm{g})+\mathrm{O}_{2}(\mathrm{~g}) \rightarrow 2 \mathrm{NO}_{2}(\mathrm{~g})$ | | $\Delta \mathrm{H}^{\circ}=$ ??? | |
Attachments
6 months agoReport content
Answer
Full Solution Locked
Sign in to view the complete step-by-step solution and unlock all study resources.
Step 1I'll solve these reactions using the standard enthalpies of formation method.
General Formula: $$\Delta H^{\circ}_{\text{reaction}} = \sum n \Delta H^{\circ}_f(\text{products}) - \sum m \Delta H^{\circ}_f(\text{reactants})
I'll break down each reaction step-by-step.
Step 2: \mathrm{NaOH}(\mathrm{s}) + \mathrm{HCl}(\mathrm{g}) \rightarrow \mathrm{NaCl}(\mathrm{s}) + \mathrm{H}_{2}\mathrm{O}(\mathrm{g})
= -133.8 \text{ kJ/mol}
Final Answer
1. \Delta H^{\circ} = - 133.8 \text{ kJ/mol} 2. \Delta H^{\circ} = - 566.0 \text{ kJ/mol} 3. \Delta H^{\circ} = - 890.3 \text{ kJ/mol} 4. \Delta H^{\circ} = - 1123.6 \text{ kJ/mol} 5. \Delta H^{\circ} = - 113.0 \text{ kJ/mol}
Need Help with Homework?
Stuck on a difficult problem? We've got you covered:
- Post your question or upload an image
- Get instant step-by-step solutions
- Learn from our AI and community of students