QQuestionAnatomy and Physiology
QuestionAnatomy and Physiology
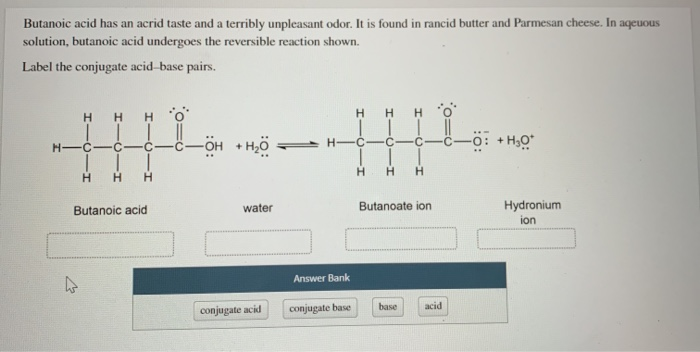
Butanoic acid has an acrid taste and a terribly unpleasant odor. It is found in rancid butter and Parmesan cheese. In aqueous solution, butanoic acid undergoes the reversible reaction shown.
Label the conjugate acid-base pairs.
Butanoic acid | water | Butanoate ion | Hydronium ion
| Answer Bank | |
| --- | --- |
| conjugate acid | |
| conjugate base | |
| base | |
Attachments
6 months agoReport content
Answer
Full Solution Locked
Sign in to view the complete step-by-step solution and unlock all study resources.
Step 1: Identify the acid and base in the given reaction.
In this reaction, butanoic acid is acting as an acid because it donates a proton (H+) to water, which acts as a base by accepting the proton.
Step 2: Write the dissociation equation for butanoic acid.
Butanoic acid (HA) dissociates into butanoate ion (A-) and a hydrogen ion (H+), which then combines with water to form hydronium ion (H^3O+). \mathrm{HA}(aq) + \mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{O}(l) \rightleftharpoons \mathrm{A}^{-}(aq) + \mathrm{H}_3 \mathrm{O}^{+}(aq)
Final Answer
conjugate acid: Hydronium ion (H^3O+) conjugate base: Butanoate ion (A-) base: Water (H^2O)
Need Help with Homework?
Stuck on a difficult problem? We've got you covered:
- Post your question or upload an image
- Get instant step-by-step solutions
- Learn from our AI and community of students