QQuestionAnatomy and Physiology
QuestionAnatomy and Physiology
Q^5.1. Which of the following is FALSE?
- If a genetic disease reduces fertility and the allele that causes the disease offers no other advantage, the allele will likely eventually disappear, due to natural selection.
- Natural selection does not favor individuals who are homozygous for the sickle-cell allele, because these individuals typically like before they are old enough to reproduce.
- Individuals who are heterozygous HbA/HbS are protected from malaria, and this is why sickle-cell disease persists in wetter, mosquito-prone regions in Africa.
- In regions where malaria does not occur, individuals who are heterozygous HbA/HbS have a fitness advantage over those who are homozygous for the normal hemoglobin allele (HbA).
Q^5.2. AFTER malaria is cured, the frequency of the HbS allele should decrease in regions with lots of mosquitoes because:
- People will no longer die from sickle-cell disease in these regions.
- Having one copy of the HbS allele will no longer be advantageous in these regions.
- Natural selection will no longer act on the HbS allele at all in these regions.
- All alleles associated with genetic diseases eventually disappear.
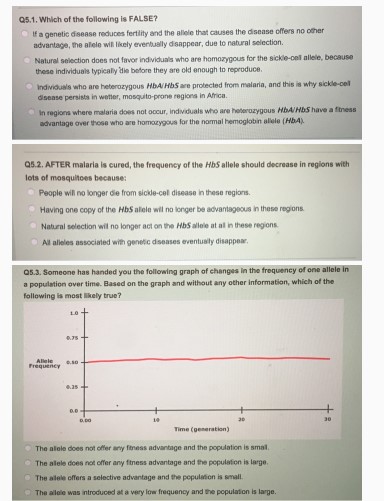
Q^5.3. Someone has handed you the following graph of changes in the frequency of one allele in a population over time. Based on the graph and without any other information, which of the following is most likely true?
- The allele does not offer any fitness advantage and the population is small.
- The allele does not offer any fitness advantage and the population is large.
- The allele offers a selective advantage and the population is small.
- The allele was introduced at a very low frequency and the population is large.
Attachments
6 months agoReport content
Answer
Full Solution Locked
Sign in to view the complete step-by-step solution and unlock all study resources.
Step 1: Identify the false statement in Q^5.1.
The first statement is true: if a genetic disease reduces fertility and the allele that causes the disease offers no other advantage, the allele will likely eventually disappear due to natural selection.
Final Answer
The first statement is true: if a genetic disease reduces fertility and the allele that causes the disease offers no other advantage, the allele will likely eventually disappear due to natural selection.
Need Help with Homework?
Stuck on a difficult problem? We've got you covered:
- Post your question or upload an image
- Get instant step-by-step solutions
- Learn from our AI and community of students