QQuestionAnatomy and Physiology
QuestionAnatomy and Physiology
# True/False
11 True or False? In stratified sampling, the population is split into non-overlapping groups or strata (e.g., men and women; people under 30 years of age and people 30 years of age and older) and then sample within each strata.
True
12 True or False? Sensitivity and specificity are both forms of conditional probability.
Attachments
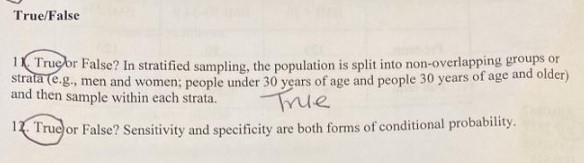
6 months agoReport content
Answer
Full Solution Locked
Sign in to view the complete step-by-step solution and unlock all study resources.
Step 1I'll solve this problem step by step, focusing on the two true/false questions about sampling and probability.
Question 11: In stratified sampling, the population is split into non-overlapping groups or strata (e.g., men and women; people under 30 years of age and people 30 years of age and older) and then sample within each strata.
Step 2: Understand the definition of stratified sampling
- Stratified sampling involves dividing the entire population into distinct, non-overlapping subgroups called strata - These strata are typically based on specific characteristics like gender, age, income, etc. - Samples are then independently drawn from each stratum
Final Answer
Question 12: Sensitivity and specificity are both forms of conditional probability. Step 1: Define sensitivity - Sensitivity measures the proportion of true positive cases correctly identified by a test - Mathematically: Sensitivity = \frac{True Positives}{True Positives + False Negatives} Step 2: Define specificity - Specificity measures the proportion of true negative cases correctly identified by a test - Mathematically: Specificity = \frac{True Negatives}{True Negatives + False Positives} Step 3: Analyze the nature of sensitivity and specificity - Both sensitivity and specificity are calculated using conditional probabilities - They represent the probability of a test result given a known condition - They are both conditional probability measures
Need Help with Homework?
Stuck on a difficult problem? We've got you covered:
- Post your question or upload an image
- Get instant step-by-step solutions
- Learn from our AI and community of students