QQuestionAnatomy and Physiology
QuestionAnatomy and Physiology
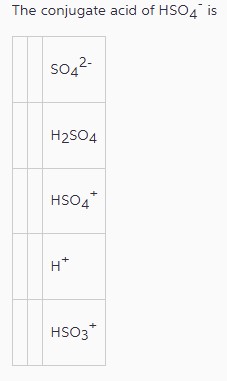
The conjugate acid of $\mathrm{HSO}_{4}{ }^{-}$is
| | $\mathrm{SO}_{4}{ }^{2 -}$ |
| --- | --- |
| | $\mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{SO}_{4}$ |
| | $\mathrm{HSO}_{4}{ }^{+}$ |
| | $\mathrm{H}^{+}$ |
| | $\mathrm{HSO}_{3}{ }^{+}$ |
Attachments
6 months agoReport content
Answer
Full Solution Locked
Sign in to view the complete step-by-step solution and unlock all study resources.
Step 1I'll solve this step-by-step using the guidelines you specified:
Step 2: Understand the Definition of Conjugate Acid
- A conjugate acid is formed when a base accepts a proton ($$\mathrm{H}^{+}$$)
- We need to determine which species is formed by adding a proton to \mathrm{HSO}_{4}^{-}
Final Answer
\mathrm{H}_{2}\mathrm{SO}_{4} is the conjugate acid of \mathrm{HSO}_{4}^{-}.
Need Help with Homework?
Stuck on a difficult problem? We've got you covered:
- Post your question or upload an image
- Get instant step-by-step solutions
- Learn from our AI and community of students