QQuestionInformation Technology
QuestionInformation Technology
Write a java code using the luhn checksum validation algorithm to check whether a credit card is valid or fake
Example of execution of the algorithm:
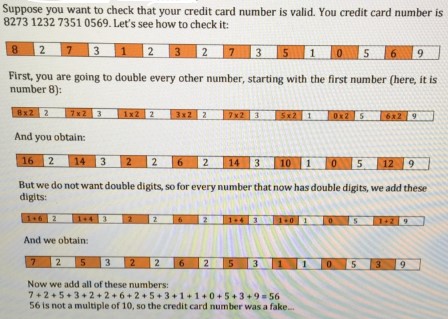
Suppose you want to check that your credit card number is valid. You credit card number is 8273123273510569 . Let's see how to check it:
| 0 | 2 | 7 | 3 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 2 | 7 | 3 | 5 | 1 | 0 | 5 | 6 | 9 |
| --- | --- | --- | --- | --- | --- | --- | --- | --- | --- | --- | --- | --- | --- | --- | --- |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
First, you are going to double every other number, starting with the first number (here, it is number 8):
| 0x^2 | 2 | 7x^2 | 3 | 1x^2 | 2 | 3x^2 | 2 | 7x^2 | 3 | 5x^2 | 1 | 0x^2 | 5 | 6x^2 | 9 |
| --- | --- | --- | --- | --- | --- | --- | --- | --- | --- | --- | --- | --- | --- | --- | --- |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
And you obtain:
| 16 | 2 | 14 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 6 | 2 | 14 | 3 | 10 | 1 | 0 | 5 | 12 | 9 |
| --- | --- | --- | --- | --- | --- | --- | --- | --- | --- | --- | --- | --- | --- | --- | --- |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
But we do not want double digits, so for every number that now has double digits, we add these digits:
| 1 + 6 | 2 | 1 + 4 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 6 | 2 | 1 + 4 | 3 | 1 + 8 | 1 | 0 | 5 | 1 + 2 | 9 |
| --- | --- | --- | --- | --- | --- | --- | --- | --- | --- | --- | --- | --- | --- | --- | --- |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
And we obtain:
| 7 | 2 | 5 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 6 | 2 | 5 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 5 | 3 | 9 |
| --- | --- | --- | --- | --- | --- | --- | --- | --- | --- | --- | --- | --- | --- | --- | --- |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Now we add all of these numbers: $7 + 2 + 5 + 3 + 2 + 2 + 6 + 2 + 5 + 3 + 1 + 1 + 0 + 5 + 3 + 9 = 1$ 56 is not a multiple of 10 , so the credit card number was a fake.
Attachments
5 months agoReport content
Answer
Full Solution Locked
Sign in to view the complete step-by-step solution and unlock all study resources.
Step 1Here's a Java implementation of the Luhn algorithm for credit card validation:
```java public class CreditCardValidator { public static boolean isValidCreditCard(String cardNumber) { // Step 1: Remove any spaces or hyphens from the card number cardNumber = cardNumber.replaceAll("[\s-]", ""); // Step 2: Check if the card number contains only digits if (!cardNumber.matches("\d+")) { return false; } // Step 3: Convert the card number to an array of digits int[] digits = new int[cardNumber.length()]; for (int i = 0; i < cardNumber.length(); i++) { digits[i] = Character.getNumericValue(cardNumber.charAt(cardNumber.length() - 1 - i)); } // Step 4: Apply Luhn algorithm int sum = 0; for (int i = 0; i < digits.length; i++) { int digit = digits[i]; // Double every second digit from right to left if (i % 2 == 1) { digit *= 2; // If doubled digit is two digits, sum its digits if (digit > 9) { digit = digit / 10 + digit % 10; } } sum += digit; } // Step 5: Check if sum is divisible by 10 return (sum % 10 == 0); } public static void main(String[] args) { // Test cases String validCard = "4111111111111111"; String invalidCard = "8273123273510569"; System.out.println("Valid Card: " + isValidCreditCard(validCard)); System.out.println("Invalid Card: " + isValidCreditCard(invalidCard)); } } ``` Let's break down the Luhn algorithm implementation:
Step 2: Preprocessing
- Remove any spaces or hyphens from the card number - Ensure the card number contains only digits
Final Answer
Space Complexity: O(n) to store the digit array
Need Help with Homework?
Stuck on a difficult problem? We've got you covered:
- Post your question or upload an image
- Get instant step-by-step solutions
- Learn from our AI and community of students