Page 1
Loading page image...
Page 2
Loading page image...
Page 3
Loading page image...
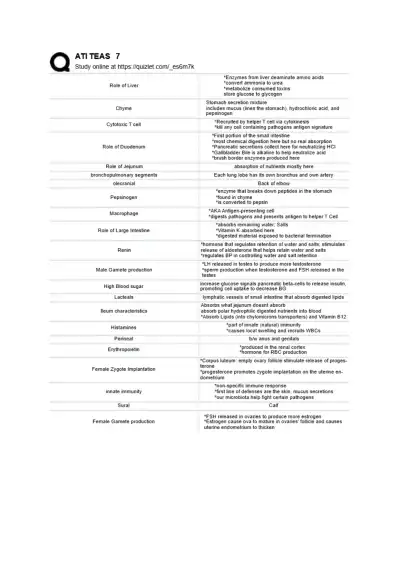
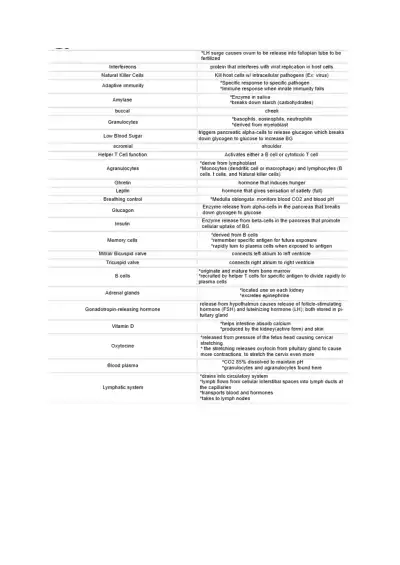
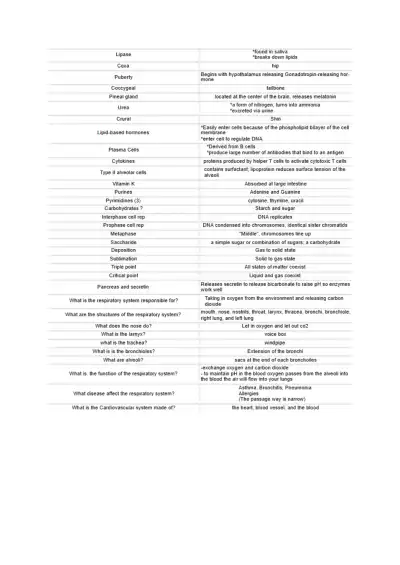
Comprehensive TEAS 7 science review: liver function, digestion, immunity, hormones, anatomy & chemistry. Key terms and explanations to help you master core exam topics efficiently.
Loading page image...
Loading page image...
Loading page image...
This document has 10 pages. Sign in to access the full document!