Page 1
Loading page ...
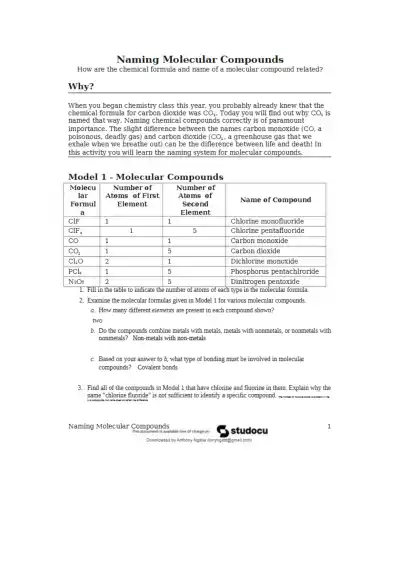
This worksheet teaches students how to name molecular compounds using prefixes and formulas. It emphasizes the importance of precise chemical naming and explores covalent bonding between nonmetals through examples like CO and CO₂.

Loading page ...
This document has 6 pages. Sign in to access the full document!