Define General Formula
An algebraic formula that can describe any member of a family of compounds
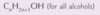
Key Terms
Define General Formula
An algebraic formula that can describe any member of a family of compounds
Define Empirical formula
Simplest ratio of atoms of each element in a compound
Define Molecular formula
Actual number of atoms of each element in a molecule
Define Structural Formula
Shows the atoms carbon by carbon + attached hydrogens & functional groups
Define Skeletal Formula
Shows the bonds of the carbon skeleton ONLY + any functional groups
Define Displayed Formula
Shows how all the atoms are arranged and all the bonds between them
Related Flashcard Decks
Study Tips
- Press F to enter focus mode for distraction-free studying
- Review cards regularly to improve retention
- Try to recall the answer before flipping the card
- Share this deck with friends to study together
| Term | Definition |
|---|---|
Define General Formula | An algebraic formula that can describe any member of a family of compounds |
Define Empirical formula | Simplest ratio of atoms of each element in a compound |
Define Molecular formula | Actual number of atoms of each element in a molecule |
Define Structural Formula | Shows the atoms carbon by carbon + attached hydrogens & functional groups |
Define Skeletal Formula | Shows the bonds of the carbon skeleton ONLY + any functional groups |
Define Displayed Formula | Shows how all the atoms are arranged and all the bonds between them |
What is the functional group for alkanes? | C—C |
What is the functional group for alkenes? | C=C |
What is the functional group for alcohols? | C—OH |
What is the functional group for haloalkanes? | C—halogen |
What is the functional group for aldehydes? | |
What is the functional group for ketones? | |
What is the functional group for carboxylic acids? | |
What is the functional group for nitriles? | |
What is the functional group for amines? | |
What is suffix for alkenes? | -ene |
What is suffix & prefix for alcohols? | -ol & hydroxy- |
What is the prefix for haloalkanes? |
|
What is the suffix for aldehydes? | -(an)al |
What is the prefix & suffix for ketones? | oxo- & -(an)one |
What is the suffix for carboxylic acids? | -(an)oic acid |
What is the suffix for nitriles? | -(anen)nitrile |
What is the prefix & suffix for amines? | -(yl)amine & amino- |
What is the general formula for alkanes? | CnH2n+2 (n = 1,2,3 etc.) |
What is the general formula for alkenes? | CnH2n (n = 1,2,3 etc.) |
What is the general formula for alcohols? | CnH2n+1OH (n = 1,2,3 etc.) |
What is the general formula for carboxylic acids? | CnH2n+1COOH (n = 0,1,2 etc.) |
What is the general formula for haloalkanes? | CnH2n+1X (n = 1,2,3 etc.) (X = F, Cl etc.) |
What is the general formula for primary amines? | CnH2n+1NH2 (n = 1,2,3 etc.) |
What is the general formula for aldehydes? | CnH2n+1CHO (n = 0,1,2 etc.) |
What is the general formula for ketones? | CmH2m+1COCnH2n+1 (m & n = 0,1,2 etc.) |
Name 5 features of a homologous series |
|
What effect does the length of the carbon chain have on chemical reactivity of the functional group? | Has little effect |
What affects the physical properties (e.g. melting/boiling point & solubility) of carbon molecule? | The length of carbon chain |
In general: small molecules are ___ and larger ones are ____ + _____ | gas & liquids + solids |
Why does the length of the carbon chain affect physical properties? | Melting/boiling points increase by small amounts as no. of C in chain increases ∵ intermolecular forces increase |
How does chain branching generally affect melting points and why? | Reduces melting points ∵ less surface area (molecules pack together less well) & weaker van der Waals forces |
Hydrogen ring molecules have prefix of ____ | 'cyclo' |
What are isomers? | Molecules that have the same molecular formula but their atoms are arranged differently |
Name 2 type of isomers | Stereoisomers & structural isomers |