A-level Chemistry: 3.3.9 Carboxylic Acids and Derivatives
This flashcard set covers key functional groups and naming conventions for esters and acyl chlorides. It includes visual representations of their functional groups and highlights the correct IUPAC suffixes and prefixes used in organic nomenclature.
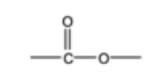
Draw the functional group of esters
Key Terms
Draw the functional group of esters
State the prefix / suffix of esters
-yl –oate
Draw the functional group of acyl chlorides
State the suffix of acyl chlorides
-oyl chloride
Draw the functional group of amides
State the suffix of amides
Related Flashcard Decks
Study Tips
- Press F to enter focus mode for distraction-free studying
- Review cards regularly to improve retention
- Try to recall the answer before flipping the card
- Share this deck with friends to study together
| Term | Definition |
|---|---|
Draw the functional group of esters | |
State the prefix / suffix of esters | -yl –oate |
Draw the functional group of acyl chlorides | |
State the suffix of acyl chlorides | -oyl chloride |
Draw the functional group of amides | |
State the suffix of amides | |
Draw the functional group of acid anhydrides | |
State the suffix of acid anhydrides | |
Weak acids partially dissociate into ______ ion and ___ ion | Partially dissociate into carboxylate ion and H+ ion |
Write an equation to represent the dissociation of weak acids. Draw the displayed formula of the molecules. | Equation: CH₃COOH ⇌ CH₃COO⁻ + H⁺ Displayed formula: CH₃–C(=O)–OH ⇌ CH₃–C(=O)–O⁻ + H⁺ |
When carboxylic acids react with carbonates, what gas is formed? | Carbon dioxide (CO₂) |
When carboxylic acids react with alcohols, what do they form? | Esters |
What functional group do esters have? | -COO- |
Describe how esters are made |
|
Give an example of an acid catalyst that can be used in esterification | Concentrated sulfuric acid |
Write an equation for when alcohols react with carboxylic acids. Draw the molecules in displayed formula. | Equation: CH₃COOH + CH₃CH₂OH ⇌ CH₃COOCH₂CH₃ + H₂O Displayed formula: CH₃–C(=O)–OH + CH₃–CH₂–OH ⇌ CH₃–C(=O)–O–CH₂–CH₃ + H–OH |
Write an equation for when ethanoic acid reacts with ethanol. Draw the molecules in displayed formula. State the name of the ester. | ethyl ethanoate 1st part = alcohol 2nd part = carboxylic acid |
Name 4 uses of esters |
|
Explain why esters make good solvents |
|
Explain how esters act as plasticisers | Added to plastics during polymerisation to make plastic more flexible |
What happens to plastics over time after they have undergone polymerisation? | Over time, plasticiser molecules escape and plastic becomes brittle and stiff |
How do you convert an ester into an alcohol? | Hydrolysis |
Why is water not used when hydrolysing esters to alcohols? Name what substances you can use instead. | Using water to split up a substance is very slow, so an acid or alkali is often used to speed it up |
Esters are Hydrolysed to form Alcohols Name 2 types of hydrolysis that can be used |
|
Describe how you can use acid hydrolysis to form an alcohol |
|
Describe how you can use base hydrolysis to form an alcohol |
|
Write an equation to show ethyl ethanoate undergoing acid hydrolysis. Draw molecules in displayed formula. | Equation: CH₃COOCH₂CH₃ + H₂O ⇌ CH₃COOH + CH₃CH₂OH Displayed formula: CH₃–C(=O)–O–CH₂–CH₃ + H–OH ⇌ CH₃–C(=O)–OH + CH₃–CH₂–OH |
Write an equation to show ethyl ethanoate undergoing base hydrolysis. Draw molecules in displayed formula. | Equation: CH₃COOCH₂CH₃ + OH⁻ → CH₃COO⁻ + CH₃CH₂OH Displayed formula: CH₃–C(=O)–O–CH₂–CH₃ + OH⁻ → CH₃–C(=O)–O⁻ + CH₃–CH₂–OH |
What are fatty acids essentially? | long chain carboxylic acids |
What is formed when fatty acids combine with glycerol? | Esters = fats and oils |
Fatty acids can be or _______ | Fatty acids can be saturated (no double bonds) or unsaturated (C=C double bonds) |
Most of fat or oil is made from _ _____ chains | fatty acid They give them many of their properties |
What type of hydrocarbon chains do animal fats have? | Have mainly saturated hydrocarbon chains |
What type of hydrocarbon chains do vegetable oils have? | Have unsaturated hydrocarbon chains |
Explain why animal fats are solid at room temperature |
|
Explain why vegetable oils are liquid at room temperature |
|
Draw an ester of glycerol and fatty acids | Here’s the displayed formula for an ester formed between glycerol and three fatty acid molecules (a triglyceride): Displayed formula: HO–CH₂–CH(OH)–CH₂–OH + 3 R–COOH → CH₂–O–CO–R |
Describe how you can hydrolyse vegetable oils and animal fats and what this produces |
|
Why are vegetable oils converted into biodiesel, before they can be used as vehicle fuels? | Vegetable oils can't be burned directly in engines |
Describe how vegetable oils are converted into biodiesel |
|
Write an equation representing vegetable oils being converted into biodiesel. Draw molecules in displayed formula. | Equation: Vegetable oil (triglyceride) + 3 CH₃OH → 3 CH₃–(CH₂)ₙ–COOCH₃ + CH₂OH–CHOH–CH₂OH Displayed formula: CH₂–O–CO–R |
State the functional groups of acyl chlorides | COCl |
Name this molecule | |
Name this molecule | |
Name 4 substances acyl chlorides react with |
|
Describe how acyl chlorides react with water. Include its product. | A vigorous reaction with cold water, producing a carboxylic acid |
Write an equation representing how ethanoyl chloride reacts with water. Draw the molecules in displayed formula. | |
Describe how acyl chlorides react with alcohols. Include its product. | A vigorous reaction at room temperature, producing an ester |
Write an equation representing how ethanoyl chloride reacts with methanol. Draw the molecules in displayed formula. | |
Describe how acyl chlorides react with ammonia. Include its product. | A violent reaction at room temperature, producing an amide |
Write an equation showing how ethanoyl chloride reacts with ammonia. Draw the molecules in displayed formula. | |
Describe how acyl chlorides react with primary amines. Include its product. | A violent reaction at room temperature, producing an N-substituted amide |
Write an equation to show how ethanoyl chloride reacts with methylamine. Draw the molecules in displayed formula. | |
What happens in each reaction with acyl chlorides? | Cl is substituted by oxygen or nitrogen group & misty fumes of hydrogen chloride are given off |
Acyl chlorides and ___ _______ react in the same way | Acid Anhydrides |
What are acid anhydrides made from? | 2 identical carboxylic acid molecules |
State how you would name an acid anhydride if you know the name of the carboxylic acid | take away 'acid' and add 'anhydride' |
Write an equation representing 2 ethanoic acids combining to form an acid anhydride. Draw the molecules in displayed formula. | |
Describe how reactions of acyl chlorides differ from reactions of acid anhydrides | Almost the same as those of acyl chlorides but reactions a less vigorous & get carboxylic acid formed instead of HCl |
Write an equation representing how ethanoic anhydride reacts with methanol | |
What mechanism reaction are acyl chloride reactions? | Nucleophilic Addition-Elimination |
Explain why acyl chlorides are easily attacked by nucleophiles | Both chlorine and oxygen draw electrons towards themselves, so carbon has slight positive charge |
Draw the mechanism for nucleophilic addition-elimination reaction between ethanoyl chloride and methanol | |
Draw the nucleophile for water | H2O: |
Draw the nucleophile for ammonia | :NH3 |
Draw the mechanism for when methyamine reacts with ethanoyl chloride | |
Aspirin is an ___ | ester |
Describe how aspirin is made | Made by reacting salicylic acid with ethanoic anhydride or ethanoyl chloride |
Why is ethanoic anhydride used in industry to make aspirin instead of ethanoyl chloride? |
|
Purifying Organic Compounds State when you can use separation | If product is insoluble in water, can use separation to remove any impurities that do dissolve in water |
Purifying Organic Compounds Describe a method for separation |
|
Purifying Organic Compounds State a method you can use to separate your product and impurities if they are both soluble in water | Solvent extraction | (similar separation method) |
Purifying Organic Compounds Describe a solvent extraction method |
|
If you use separation to purify a product, why does the product have to be dried? | ∵ organic layer will end up containing trace amounts of water |
Describe how you can remove water from a purified product by drying it |
|
When removing water from a purified product by drying it, why is anhydrous salt used? | Salt is used as drying agent = binds to any water present to become hydrated |
Describe a way, other than by drying it, to remove impurities from a product of a reaction. |
|
Describe how you could remove acid from an impure product in solution. |
|
How can volatile liquids can be purified? | By distillation |
Describe how distillation works |
|
Describe how you can purify volatile liquids by distillation |
|
When purifying volatile liquids by distillation, why should you use an electric heater? | Many organic chemicals are flammable |
State how organic solids can be purified | Recrystallisation |
Describe how organic solids can be purified via recrystallisation |
|
Describe how you could remove liquid containing soluble impurities from crystals by filtering a mixture under reduced pressure | Pour mixture into filter paper lined Büchner funnel (flat bottomed funnel with holes in base) that's sitting in side-arm flask attached to vacuum line |
Recrystallisation Why does crystals of product form as the solution cools? |
|
What are good indicators of purity? | Melting and boiling points |
Pure substances have melting and boiling points | specific |
What happens to substance's melting and boiling point when it's impure? | Melting point is lowered and boiling point is raised |
What happens substance's melting and boiling point when it's very impure? | Melting and boiling will occur across a wide range of temperatures |
What type of apparatus can you use to accurately determine the melting point of an organic solid? | Melting point apparatus |
Describe how you can use melting point apparatus to accurately determine the melting point of an organic solid |
|
Pure substances melt _____ | sharply |
Give an observation that occurs during esterification | Sweet smell/oily layer |
Recrystallisation Why shouldn't you add too much solvent when dissolving the solid? | Want saturated solution of impure product |
Recrystallisation Why do you filter hot solution through a heated funnel? | To remove any insoluble impurities |
Recrystallisation Why do you leave the solution to cool down slowly? | More crystals of product will form as it cools/decreases solubility of solid |
Recrystallisation Why do you filter the mixture under reduced pressure? | To remove liquid containing soluble impurities from crystals |
Recrystallisation Why do you wash the crystal with ice-cold solvent? | To remove any soluble impurities from their surface |