Organic Chemistry ACS Final Exam
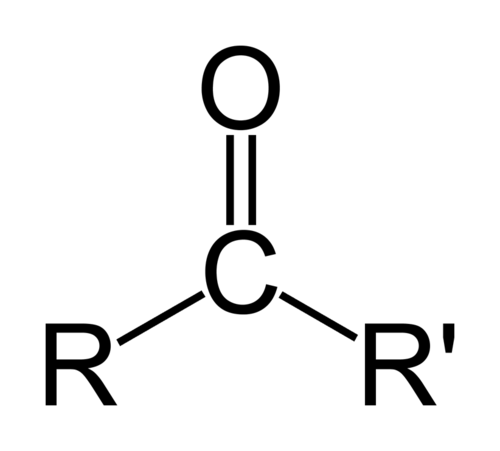
The general structure of a ketone, an organic compound characterized by a carbonyl group (C=O) bonded to two carbon-containing groups (R and R′). Ketones are important functional groups commonly found in biochemistry and synthetic organic chemistry, and are frequently tested on the ACS Organic Chemistry Final Exam.
ketone
Key Terms
Related Flashcard Decks
Study Tips
- Press F to enter focus mode for distraction-free studying
- Review cards regularly to improve retention
- Try to recall the answer before flipping the card
- Share this deck with friends to study together
| Term | Definition |
|---|---|
ketone | |
aldehyde | |
carboxylic acid | |
ester | |
amide | |
anhydride | |
amine | |
ether | |
constitutional isomers | same formula, different connectivity |
stereoisomers | same formula, different spatial arrangement |
enantiomers | non-superimposable mirror images |
diastereomers | stereoisomers that are not mirror images of each other |
R configuration | clockwise |
S configuration | counter clockwise |
what functional groups does a peptide bond contain | amide |
what functional groups does a lipid contain | esters |
what functional groups do amino acids contain? | aromatic rings |
meso compound | molecule with multiple stereo centers and it is superimposable on its mirror image |
NO2 prefix | nitro |
CH=CH2 prefix | vinyl |
CH2CH=CH2 prefix | allyl |
phenol | |
benzoic acid | |
aniline | |
toluene | |
three types of disubstituted benzenes | ortho-1,2 |
benzene | |
as you increase heat of combustion, what happens stability? | it decreases |
Carbon 13 NMR Resonances | 0-80 sp3c |
H 1 NMR Resonances | 0.9-1.5 sp3 C |
IR Resonances | 3400 OH and NH |
what is the difference between phenyl and benzyl? | benzyl has CH2 in between the ring and the substituted chain |
bond angle for sp2 hybridized? | 109.5 |
what are 2 key things to lewis structures? | 1. filled octets |
if a ring has a charge, then it is ____ | aromatic |
a strong acid corresponds to? | a weak base |
what does a double bond right next to acidic H mean? | it is more acidic |
low pKa value means it is... | more acidic |
how does hybridization relate to acidity? | the more S character it is, the more acidic |
a hydrogen next to an electronegative atom will always be... | more acidic |
how do you determine if molecules are meso isomers? | needs to be chiral and needs to have a plane of symmetry |
how do you find most stable newman projection? | it will have less gauche interactions |
what are wedges and dashes in fischer projections? | horizontal-wedge |
if only one stereo center is flipped in a molecule, they are... | diastereomers |
do racemic mixtures get plane polarized light? | no, they cancel each other out |
do meso compounds get plane polarized light? | no, they cannot bend light |
what can triple bonds not do stereoisomerically? | exhibit cis or trans |
what can an enantiomer not have? | a plane of symmetry |
what happens with a dehydrohalogenation reaction? | H wants to attack and form a double bond to increase stability |
a strong acid corresponds to a ________ nucleophile | weak |
how do you tell if it is a syn or anti addition? | Syn- two atoms are either both forward/back |
where does hydroboration put the substituent? | on the less substituted side (anti-markovnikov) |
what are the most stable types of free radicals? | allylic or benzylic |
what are the 3 steps of a free radical reaction? | initiation-goes from 0-1 radicals |
what is the energy of propagations like? | very low activation energy |
what does non-regioselective mean in terms of energy? | it goes down in energy |
what does it mean if an alcohol absorbance peak on the IR spectrum is abnormally wide? | it is a carboxylic acid |
what does chromic acid do? | it turns C-H bonds into C-O bonds |
E2 reactions favor ______ alkyl halides | tertiary |
what is the trick for predicting major products of E2 reactions? | if the base is sterically hindered, then the major product will be the LESS substituted alkene |
what is the reagent BH3 * THF used for? | hydroboration-oxidation |
how could you tell if a pair were resonance structures? | atoms cannot be moved, only pi bonds and lone pairs |
which is more acidic: OH or NH? | OH |
which hybridization is the most acidic? | sp>sp2>sp3 |