Periodic Table
This flashcard set introduces the periodic table, explaining its structure (groups and periods), the classification of elements, and key physical and chemical properties. It also includes foundational facts like the invention of the periodic table by Dmitri Mendeleev and highlights special element groups like the noble gases.
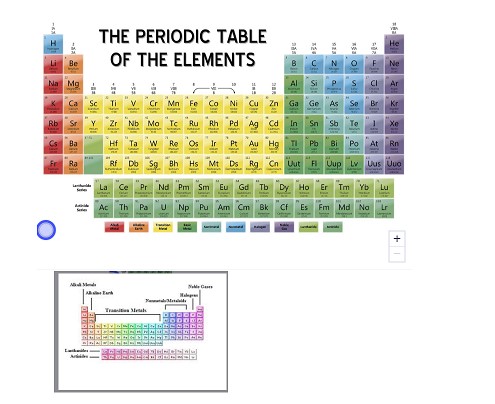
Periodic table
A chart that organizes the elements by their chemical properties and increasing atomic number
Key Terms
Periodic table
A chart that organizes the elements by their chemical properties and increasing atomic number
Element
Pure substance that consists entirely of one type of atom
A substance that cannot be broken down into simpler substances
What are the vertical columns of the periodic table called?
The vertical columns in the periodic table are called groups.
Elements in the same group have similar chemical properties.
The group number i...
How many groups are in the periodic table?
The periodic table has eight main groups.
For example, group 1 contains very reactive metals such as sodium - Na
while group 7 contains very ...
What are the horizontal rows of the periodic table called?
Periods
Elements in the same horizontal row are said to be in the same period. The periods are numbered from top to bottom.
The period number...
How many periods are in the periodic table?
Seven periods of elements occur naturally on Earth. For period 8, which includes elements which may be synthesized after 2016, is the extended peri...
Related Flashcard Decks
Study Tips
- Press F to enter focus mode for distraction-free studying
- Review cards regularly to improve retention
- Try to recall the answer before flipping the card
- Share this deck with friends to study together
| Term | Definition |
|---|---|
Periodic table | A chart that organizes the elements by their chemical properties and increasing atomic number |
Element | Pure substance that consists entirely of one type of atom |
What are the vertical columns of the periodic table called? | The vertical columns in the periodic table are called groups. |
How many groups are in the periodic table? | The periodic table has eight main groups. |
What are the horizontal rows of the periodic table called? | Periods |
How many periods are in the periodic table? | Seven periods of elements occur naturally on Earth. For period 8, which includes elements which may be synthesized after 2016, is the extended periodic table |
Who invented the periodic table? | The Russian chemist Dmitri Mendeleev was the first scientist to make a periodic table similar to the one used today. Mendeleev arranged the elements by atomic mass. |
Physical properties | A characteristic that can be observed or measured without changing the identity of the substance |
Chemical properties | properties that can only be observed when there is a change in the composition of a substance |
Noble gases | unreactive nonmetals that are colorless and odorless gases at room temperature |
Atomic mass | Number of protons and neutrons |
RELATIVE atomic mass Ar | the weighted average of the masses of the isotopes of an element |
Atomic number | The number of protons in the nucleus of an atom |