Page 1
Loading page ...
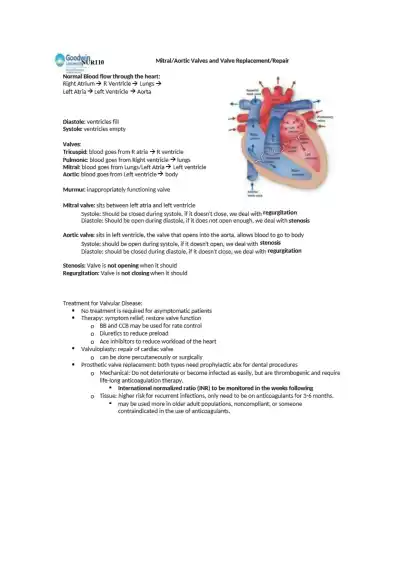
Overview of mitral and aortic valve function, valve disorders (stenosis/regurgitation), symptoms, and treatments including meds, valvuloplasty, and prosthetic valve options with nursing considerations like anticoagulation and infection prevention.

Loading page ...