Page 1

Loading page image...
Page 2

Loading page image...
Page 3

Loading page image...
Page 4

Loading page image...
Page 5
Loading page image...
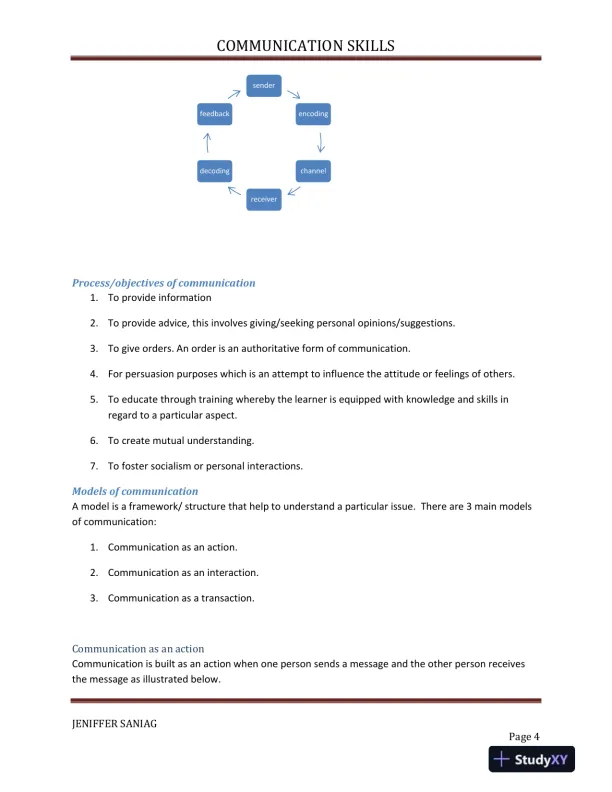
A communication study focusing on key models and overcoming workplace barriers.
Loading page image...
Loading page image...
Loading page image...
Loading page image...
Loading page image...
This document has 15 pages. Sign in to access the full document!