Page 1
Loading page image...
Page 2

Loading page image...
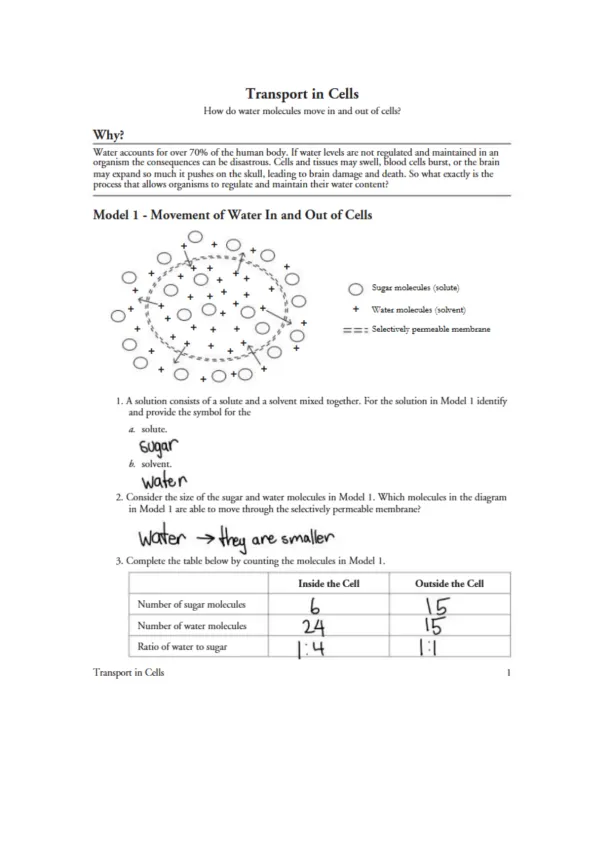
This worksheet explores how water moves in and out of cells through osmosis. Using a model with sugar and water molecules, it examines selectively permeable membranes and helps students analyze molecule movement, ratios inside outside the cell.
Loading page image...
Loading page image...
This document has 6 pages. Sign in to access the full document!