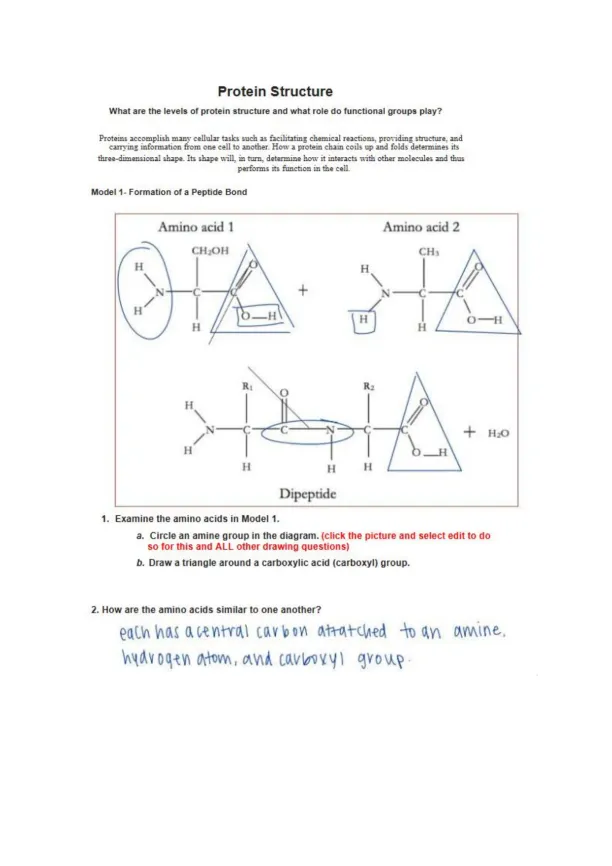
Page 1
Loading page image...
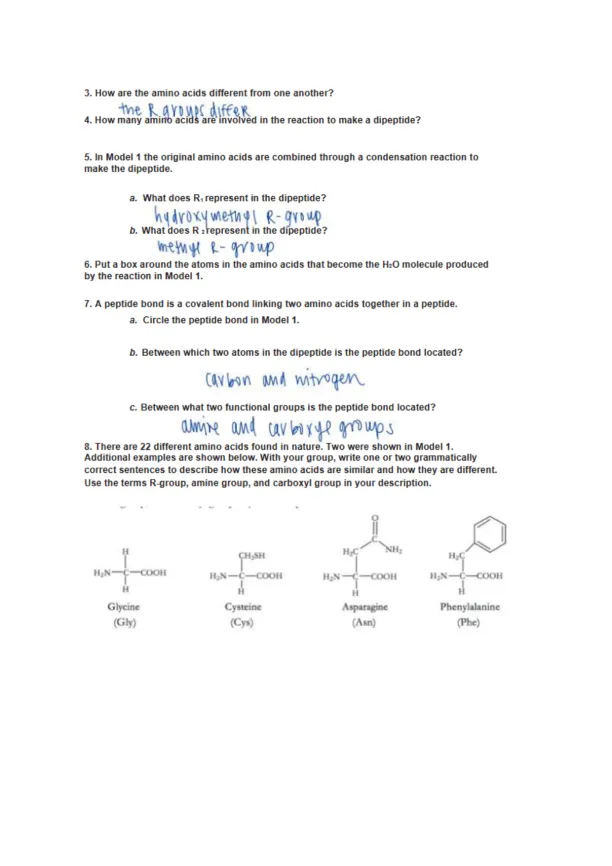
Page 2
Loading page image...
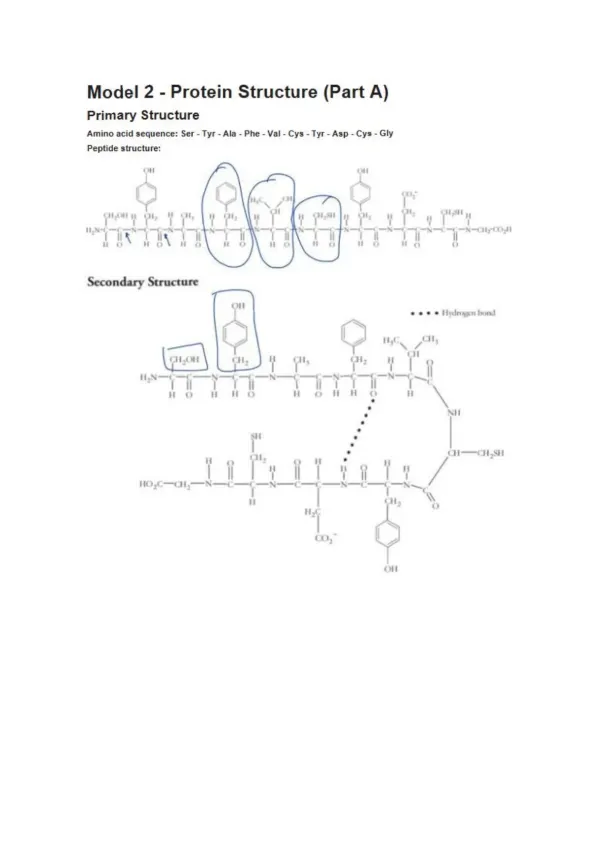
Page 3
Loading page image...
Page 4

Loading page image...
Explore the levels of protein structure and understand how functional groups like amine and carboxyl groups influence protein folding, function, and interactions.
Loading page image...
Loading page image...
Loading page image...
Loading page image...
This document has 11 pages. Sign in to access the full document!