Page 1
Loading page ...
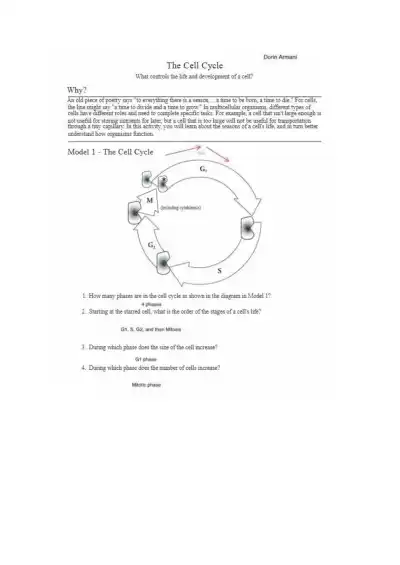
Explore the stages of the cell cycle and what controls cell growth, division, and function. Learn how cells balance size, role, and timing to support life in multicellular organisms.

Loading page ...
This document has 6 pages. Sign in to access the full document!