Page 1
Loading page ...
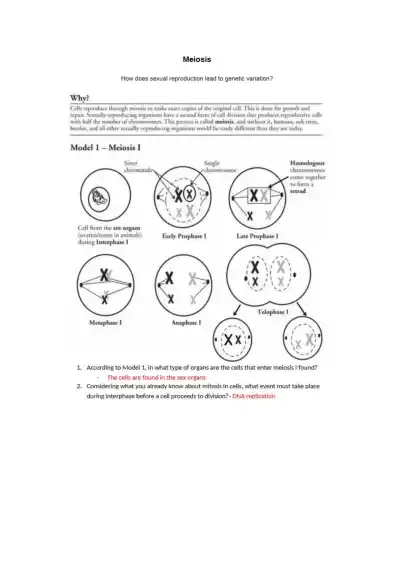
This content explains key stages of meiosis I, including chromosome replication, homologous pairing (tetrads), diploid to haploid transition, and genetic variation.

Loading page ...
This document has 8 pages. Sign in to access the full document!