A-level Biology - 3.4.8 Control of Heart Rate
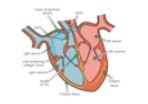
The cardiac cycle is controlled by electrical activity starting at the SAN, which causes the atria to contract. After a brief delay at the AVN, impulses travel down the bundle of His and through Purkyne tissue, triggering ventricular contraction from the base upwards. This ensures coordinated and efficient heartbeats.
Describe how the cardiac cycle is controlled by electrical activity (7x)
SAN generates waves of electrical activity across atrial walls causing atria to contract
Non-conducting tissue prevents waves of electrical activity from being passed directly from atria to ventricles
∴ Waves of electrical activity go to ventricles via AVN
Delay at AVN allows atria to completely empty before ventricles contract
AVN sends waves of electrical activity down the bundles of His (on apex)
Purkyne tissue carries waves of electrical activity into muscular walls of ventricles
Ventricles contract from the bottom upwards
Key Terms
Describe how the cardiac cycle is controlled by electrical activity (7x)
SAN generates waves of electrical activity across atrial walls causing atria to contract
Non-conducting tissue prevents waves of electrical a...
What part of the brain controls the rate at which SAN fires (i.e. heart rate)
Medulla oblongata
Why do animals need to alter their heart rate?
To respond to internal stimuli
(e.g. to prevent fainting due to low blood pressure or to make heart rate is high enough to supply body weight...
Name the receptors that detect a change from the set point (those involved in heart rate)
Baroreceptors (pressure receptors)
Chemoreceptors (chemical receptors)
Where are baroreceptors found?
Aorta
Carotid arteries (major arteries in neck)
Where are chemoreceptors found?
Aorta
Carotid arteries
Medulla
Related Flashcard Decks
Study Tips
- Press F to enter focus mode for distraction-free studying
- Review cards regularly to improve retention
- Try to recall the answer before flipping the card
- Share this deck with friends to study together
| Term | Definition |
|---|---|
Describe how the cardiac cycle is controlled by electrical activity (7x) | SAN generates waves of electrical activity across atrial walls causing atria to contract Non-conducting tissue prevents waves of electrical activity from being passed directly from atria to ventricles �∴ Waves of electrical activity go to ventricles via AVN Delay at AVN allows atria to completely empty before ventricles contract AVN sends waves of electrical activity down the bundles of His (on apex) Purkyne tissue carries waves of electrical activity into muscular walls of ventricles Ventricles contract from the bottom upwards |
What part of the brain controls the rate at which SAN fires (i.e. heart rate) | Medulla oblongata |
Why do animals need to alter their heart rate? | To respond to internal stimuli (e.g. to prevent fainting due to low blood pressure or to make heart rate is high enough to supply body weight enough oxygen) |
Name the receptors that detect a change from the set point (those involved in heart rate) | Baroreceptors (pressure receptors) Chemoreceptors (chemical receptors) |
Where are baroreceptors found? | Aorta Carotid arteries (major arteries in neck) |
Where are chemoreceptors found? | Aorta Carotid arteries Medulla |
What do baroreceptors monitor? | Blood pressure |
What do chemoreceptors monitor? | They monitor oxygen level in blood and also CO2 and pH (which are indicators of O2 level) |
Describe how the body restores blood pressure when there’s high blood pressure | Baroreceptors detect high blood pressure Impulses sent to medulla which sent impulses along parasympathetic neurones Increased frequency of impulses (to/from medulla) Secrete acetylcholine (neurotransmitter) which binds to receptors in SAN Cardiac muscles (effector) Heart rate slows down to reduce blood pressure back to normal |
Describe how the body restores blood pressure when there’s low blood pressure | Baroreceptors detect low blood pressure Impulses sent to medulla which sent impulses along sympathetic neurones Increased frequency of impulses (to/from medulla) Secrete noradrenaline which binds to receptors in SAN Cardiac muscles (effector) Heart rate speeds up to increase blood pressure back to normal |
Describe how the body restores O2/CO2/pH levels when there’s high blood O2, low CO2 or high pH levels | Chemoreceptors detect chemical changes in blood Impulses sent to medulla which sends impulses along parasympathetic neurones Increased frequency of impulses (to/from medulla) Secrete acetylcholine which bind to receptors on SAN Cardiac muscles (effector) Heart rate decreases to return O2, CO2 and pH levels back to normal |
Describe how the body restores O2/CO2/pH levels when there’s low blood O2, high CO2 or low pH levels | Chemoreceptors detect chemical changes in blood Impulses sent to medulla which sends impulses along sympathetic neurones Increased frequency of impulses (to/from medulla) Secrete noradrenaline which bind to receptors on SAN Cardiac muscles (effector) Heart rates increases to return O2, CO2 and pH levels back to normal |