Anatomy: Abdomen VII - Jejunum & Ilium
These flashcards detail the jejunum and ileum, which together make up the majority of the small intestine (~6–7 m), focusing on their anatomical distinctions, locations within the abdominal quadrants, and functional roles. The mesentery—a fan-shaped peritoneal fold—is described, including its anatomical attachments and the key structures it encloses, such as blood vessels, lymphatics, fat, and autonomic nerves.
JEJUNUM
begins at duodenojejunal flexure (alimentary tract resumes an intraperitoneal course)
jejunum + ileum = 6 - 7 m long (jejunum constituting 2/5)
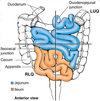
most of jejunum lies in left upper quadrant of the infracolic compartment
Key Terms
JEJUNUM
begins at duodenojejunal flexure (alimentary tract resumes an intraperitoneal course)
ILEUM
Jejunum + ileum = 6-7m long (ilium consists of 3/5)
most of the ileum ...
Differences between the jejunum and ileum:
(no clear line of demarcation)
Jejunum = site of digestion processes + secretio...
mesentery
fan-shaped fold of peritoneum; attaches jejunum + ileum to posterior abdominal wall
What is located between the 2 layers of the small intestine mesentary?
superior mesenteric vessels
lymph nodes
variable amoun...
superior mesenteric artery
supplies the jejunum + ileum
usually arises from abdominal aorta at L1 vertebra...
Related Flashcard Decks
Study Tips
- Press F to enter focus mode for distraction-free studying
- Review cards regularly to improve retention
- Try to recall the answer before flipping the card
- Share this deck with friends to study together
| Term | Definition |
|---|---|
JEJUNUM |
|
ILEUM |
- ends at ileocecal junction (union of terminal ileum + cecum) |
Differences between the jejunum and ileum: | (no clear line of demarcation)
Peyer’s patches |
mesentery | fan-shaped fold of peritoneum; attaches jejunum + ileum to posterior abdominal wall
|
What is located between the 2 layers of the small intestine mesentary? | superior mesenteric vessels lymph nodes variable amount of fat autonomic nerves |
superior mesenteric artery | supplies the jejunum + ileum
(approx 1 cm inferior to celiac trunk)
(give rise to straight arteries = vasa recta) |
superior mesenteric vein | drains jejunum + ileum
|
LACTEALS |
|
Within the mesentery, the lymph passes sequentially through what three groups of lymph nodes? | Juxta-intestinal lymph nodes: located close to the intestinal wall Mesenteric lymph nodes: scattered among the arterial arcades Superior central nodes: located along the proximal part of the superior mesenteric artery
|
SYMPATHETIC & PARASYMPATHETIC FIBERS | Sympathetic:
Parasympathetic:
- presynaptic parasympathetic fibers synapse with postsynaptic parasympathetic neurons in the myenteric and submucosal plexuses in the intestinal wall |
sympathetic stimulation … | … reduces motility of intestine + secretion; acts as a vasoconstrictor
|
Parasympathetic stimulation | … increases motility of intestine + secretion, restoring digestive activity following a sympathetic reaction * also has sensory (visceral afferent) fibers; insensitive to most pain stimuli, including cutting and burning; it is sensitive to distension that is perceived as colic (spasmodic abdominal pains). |
Primordial gut comprises the foregut, midgut, and hindgut. Pain in these areas arise form what structures and localizes where? | foregut derivatives: esophagus, stomach, pancreas, duodenum, liver, and biliary ducts localizes in the epigastric region midgut derivatives: small intestine distal to bile duct, cecum, appendix, ascending colon, and most of the transverse colon localizes in the periumbilical region hindgut derivatives: distal part of the transverse colon, descending colon, sigmoid colon, and rectum localizes in the hypogastric region. |
Physiological gut herniation (normal) |
|
Malrotation of the midgut |
|
Ischemia of the Intestine |
|
Ileal Diverticulum | ileal diverticulum (of Meckel) = congenital anomaly in 1 - 2% of population - remnant of proximal part of embryonic yolk stalk; diverticulum usually appears as a finger-like pouch
|