Histology - Exam 2 Assorted Images
Caveolae are small invaginations of the plasma membrane in smooth muscle cells. They function in calcium storage and signal transduction, playing a key role in contraction. Hemidesmosomes are anchoring junctions that attach epithelial cells to the basement membrane. They contain integrins that link the cytoskeleton to extracellular matrix components. Dense bodies (DB) in smooth muscle act like Z-discs, anchoring actin filaments. The nucleus appears corkscrew-shaped during contraction due to the twisting of the cell.
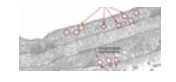
Caveolae of smooth muscle cell
Key Terms
Caveolae of smooth muscle cell
Hemidesmosomes
Smooth Muscle Fiber Cell - with dense bodies labeled DB and corckscrew nucleus
Red arrows - Ependymal cells (glial cell) line central canal of spinal cord apical surfaces has cilia.
Autonomic Ganglia - Blue arrow - sattelite cell
Desmosome (Macula adherens)
Related Flashcard Decks
Study Tips
- Press F to enter focus mode for distraction-free studying
- Review cards regularly to improve retention
- Try to recall the answer before flipping the card
- Share this deck with friends to study together
| Term | Definition |
|---|---|
Caveolae of smooth muscle cell | |
Hemidesmosomes | |
Smooth Muscle Fiber Cell - with dense bodies labeled DB and corckscrew nucleus | |
Red arrows - Ependymal cells (glial cell) line central canal of spinal cord apical surfaces has cilia. | |
Autonomic Ganglia - Blue arrow - sattelite cell | |
Desmosome (Macula adherens) | |
Red arrows-Pyramidal cells. Note processes (less extensive than Purkinje cells), cell body tends to have pyramidal appearance. | |
Peripheral Nerve | |
Autonomic ganglia - Peripheral nervous system. Differ from spinal ganglia by having multipolar neurons with dendrites. | |
Blue Arrows point to PNS Schwann Cells | |
TIght Junction (zona occludens) | |
choroid epithelial cell - neuroglia - red arrows indicate RBCs | |
Dorsal Root Ganglion (large pseudounipolar neurons - look for tightly packed neurons with lots of satellite cells) | |
Myoepthelial Cells - unlabeled arrow points to them | |
Purkinje cells (cerebellum) Red arrows -cell bodies (see large dendritic trunk with branches-tree) Blue arrows - axons of the Purkinje cells | |
Skeletal Muscle - Black Arrows are A Bands (dark staining) BLue arrows are Z lines within A bands | |
Glial cell (support of nervous system) Red arrows-astrocytes (see fine processes from cell body) | |
Carcinoma | |
Multipolar motor neuron in spinal cord. Yellow arrows - dendrites (basophilic material is Nissl substance) Green arrow - axon hillock | |
CNS Synapse - glutamate (+) GABA (-) | |
Adenoma | |
ependymal cells | |
Gap Junctions, No CAMs, cells connected via Connexion proteins, regulated opening and closing | |
top to bottom - zona occuludens, zona adherens, and macula adherens (desmosome) | |
Tight Junction (Zonula occludens, occluding junction) - No CAMS, cells connected by transmembrane proteins. ONce formed, functional polarity established. | |
Basement Membrane | |
PNS Sensory ganglia - red arrow points to capsule |