Histology - Stomach, Small and Large Intestine
The large intestine lining features enterocytes for absorption and numerous goblet cells for mucus secretion, which lubricates fecal matter. Goblet cells are especially abundant here compared to the small intestine. Enteroendocrine cells secrete hormones that regulate gut function, while M cells, found overlying Peyer’s patches, sample and transport antigens to immune cells. Notably, the large intestine lacks Paneth cells, which are typical in the small intestine.
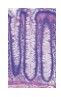
Large Intestine - ▪ Enterocytes ▪ Goblet cells
▪ Enteroendocrine cells ▪ M cells (antigen-transport)
NO paneth cells.
Key Terms
Large Intestine - ▪ Enterocytes ▪ Goblet cells
▪ Enteroendocrine cells ▪ M cells (antigen-transport)
Small Intestine
Appendix with prominent GALT - numerous lymphatic nodules.
Oblique, circular, longitudinal layers of muscularis externa in stomach.
Esophagus epithelium - Simple Squamous, Non-Keratinized.
Gastritis in lamina propria (Loose CT inflammation)
Related Flashcard Decks
Study Tips
- Press F to enter focus mode for distraction-free studying
- Review cards regularly to improve retention
- Try to recall the answer before flipping the card
- Share this deck with friends to study together
| Term | Definition |
|---|---|
Large Intestine - ▪ Enterocytes ▪ Goblet cells ▪ Enteroendocrine cells ▪ M cells (antigen-transport) NO paneth cells. | |
Small Intestine | |
Appendix with prominent GALT - numerous lymphatic nodules. | |
Oblique, circular, longitudinal layers of muscularis externa in stomach. | |
Esophagus epithelium - Simple Squamous, Non-Keratinized. | |
Gastritis in lamina propria (Loose CT inflammation) | |
Enteroendocrine cells - found at stomach glands, mostly at their base. | |
Fundus and Body with fundic glands, surface, stem cells, muscous neck cells, parietal cells, chief cells, enteroendocrine cells. | |
Parietal cells - (HCl secretion) - acidophilic, proton pumps, canaliculi, tubulovescular membranes - secreting acid. | |
Chief Cells - ABC - apical, basophilic, chief cells | |
Esophagogastric junction with esophageal cardiac glands - mucus secreting glands in the laminal propria of the lower esophagus. | |
Enteric nervous system (ENS) - regulates motility, secretion, blood flow. Responds to mechanical, chemical ANS stimuli. | |
Peyer’s patches - large accumulations of GALT in the lamina propria of ILEUM - may extend into submucosa. | |
Cardicac Gland - pale, alkaline | |
Muscularis Mucosae - agitates luminal contents, aids gland expression. Smooth muscle. Same innervation as glands. | |
Brunner’s glands (or duodenal glands) found in the duodenum which is above the hepatopancreatic sphincter. Produce a mucus-rich alkaline secretion (containing bicarbonate) in order to: protect the duodenum from the acidic content of chyme; | |
Appendix with mucosa, lamina propria, submucosa, lymphatic nodule | |
PS is pyloric sphincter - thickening of circular layer of muscularis externa | |
Appendix - Promitent GALT | |
Enteroendocrine cells - basal SGs, fundic gland. Secrete hormones like gastrin, CCK, secretin | |
Ileocecal junction | |
Adhesion of serosa or adventitia. Clinical application, fubrous scar tissue, type 1 collagen. | |
Large intestine - simple columnar, intestinal glands and goblet cells that secrete mucus for lubrication and protection. | |
Pyloric Gland | |
GALT - plasma cells, protection, abundant in ileum and appendix | |
Rectoanal Junction - Transition from simple columnar to stratified columnar to stratified squamous non keratinized | |
Top to Bottom - Mucosa, GALT, submucosa, Muscularis externa, serosa | |
Mucosa, lamina propria. (Loose CT, fenestrated cap, glands, GALT) | |
Small Intestine - with intestinal folds, villi. | |
Paneth Cell - epithelium of the small intestine located just below the intestinal stem cells in the intestinal glands (in the crypts of Lieberkühn). Large granules that consist of anti-microbial compounds important in immunity and host-defense. | |
Stomach - Pylorus - numerous glands | |
Stomach rugae. | |
Fundus (or body) of Stomach with surface mucous cells and neck cells - aka Fundic Glands within the lamina propria of fundus and body. | |
Paneth Cell - epithelium of the small intestine located in the intestinal glands (in the crypts of Lieberkühn). Large granules that consist of anti-microbial compounds important in immunity and host-defense. | |
Upper third muscularis externa in esophagus. Skeletal swallowing. Lower motor neurons, vagus nerve. neuromuscular synapse, upper esophageal sphincter. | |
Esophagus - Esophageal glands in submucosa lubricate and protect GI wall from self-digestion. | |
Intestinal glands (crypts of Lieberkühn) contains multiple types of cells: enterocytes (absorbing water and electrolytes), goblet cells (secreting mucus), enteroendocrine cells (secreting hormones), and at the base, Paneth cells (secreting anti-microbial peptides) and stem cells. | |
The black bracket is the mucosa; the blue bracket is the submucosa; the red bracket is the muscularis; the green arrow indicates the serosa. | |
Submucosa - Dense CT aids in supprt, tension. Larger vessels, give rise to capillaries. Submucosal Plexus. Involved in metastasis (lymph vessels) and hemorraging (ulcer). | |
Stomach Epithelium: simple columnar Mucosal glands: fundic, cardiac, pyloric glands NO submucosal glands. | |
Small intestine with enterocyte, goblet cell, smooth muscle, and a central lacteal. | |
Duodenum with Brunner's Glands above the hepatopancreatic sphincter (Sphincter of Oddi). The main function of these glands is to produce a mucus-rich alkaline secretion (containing bicarbonate). | |
Large Intestine - OL is outer longitundinal folded up to become teniae coli | |
Large Intestine Mucosa - no villi, plenty of glands in LP. Abundant goblet cells. Similar to small intestine, but NO paneth cells. | |
Small Intestine with circular folds and villi. Villus epithelium: ▪ Enterocytes ▪ Goblet cells Villus lamina propria: | |
Middle third transition of esophageal muscularis externa. | |
ENS Myenteric Plexus - regulates peristalsis (muscularis externa) | |
Muscularis Externa - Myenteric Plexus regulates peristalsis. Clinical - dysmotility and T2 carcinoma. |