Histology - Vasculature Images
Vasa vasorum are small blood vessels that supply the walls of large arteries and veins (like the aorta). They are visible in the tunica adventitia and provide nutrients to outer vessel layers too thick for diffusion alone. Arterioles are small arteries with a narrow lumen and 1–2 layers of smooth muscle in the tunica media. In H&E stain, they appear as round structures with a well-defined muscular wall and relatively little surrounding connective tissue.
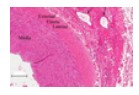
Arrows point to Vasa Vasorum
Key Terms
Arrows point to Vasa Vasorum
Arteriole - H&E
Venules
Large Vein
Example - Superior Vena Cava
Sinusoidal (discontinuous) capillary
Large irregular lumen. Discontinuous basal lamina. Foun...
Elastic (conducting) artery. 40-70 fenestrated elastic sheets. Example - aorta.
Related Flashcard Decks
Study Tips
- Press F to enter focus mode for distraction-free studying
- Review cards regularly to improve retention
- Try to recall the answer before flipping the card
- Share this deck with friends to study together
| Term | Definition |
|---|---|
Arrows point to Vasa Vasorum | |
Arteriole - H&E | |
Venules | |
Large Vein Example - Superior Vena Cava | |
Sinusoidal (discontinuous) capillary Large irregular lumen. Discontinuous basal lamina. Found in Bone marrow, liver, spleen (sites of fluid & cell migration in & out of BV). | |
Elastic (conducting) artery. 40-70 fenestrated elastic sheets. Example - aorta. | |
Fenestrated (type II) Capillary. Fenestrations, complete basal lamina. Found in endocrine organs, GI tract, kidney. | |
| |
Muscular arteries Draw blood from an elastic artery and branch into “resistance vessels” including small arteries and arterioles. They contain layers of smooth muscle. | |
muscular arteries and medium veins - often found next to each other. | |
Tunica Adventitia | |
Internal Elastic Lamina (IEL). Permits diffusinof nutrients and waste between lumen, cells in tunica intima, and the cellsin inner half of tunica media. | |
Arrows point to Weibel-Palade bodies | |
Valve leaflets Core of subendothelial CT covered by endothelium | |
Continuous (type I) Capillary - TEM | |
Muscular (distributing) artert. 5-40 layers of smooth muscle. Example - internal thoracic artery | |
Tunica Media. Smooth muscle, contractile and/or secretory, coordinate via gap junctions. | |
External Elastic Lamina (EEL) Separates tunica media from TA, secreted by smooth muscle cells of the tunica media. | |
Medium vein - example - cephalic vein | |
Precapillary sphincter - Red circle and arrows | |
Atherosclerotic Plaque - Within the tunica intima. | |
tunica adventitia | |
Continuous (type I) Capilarries - LM | |
Purkinje Fibers Modified cardiac muscle fibers, located in subendocardial, (not epithelial). Large pale-looking (“moth-eaten) cells. | |
Arteriole muscular walls (usually only one to two layers ofsmooth muscle), the primary site of vascular resistance. The greatest change in blood pressure and velocity of blood flow occurs at the transition of arterioles to capillaries. | |
|